Understanding Temporary Pacemaker Implantation (TPI) in Cardiology
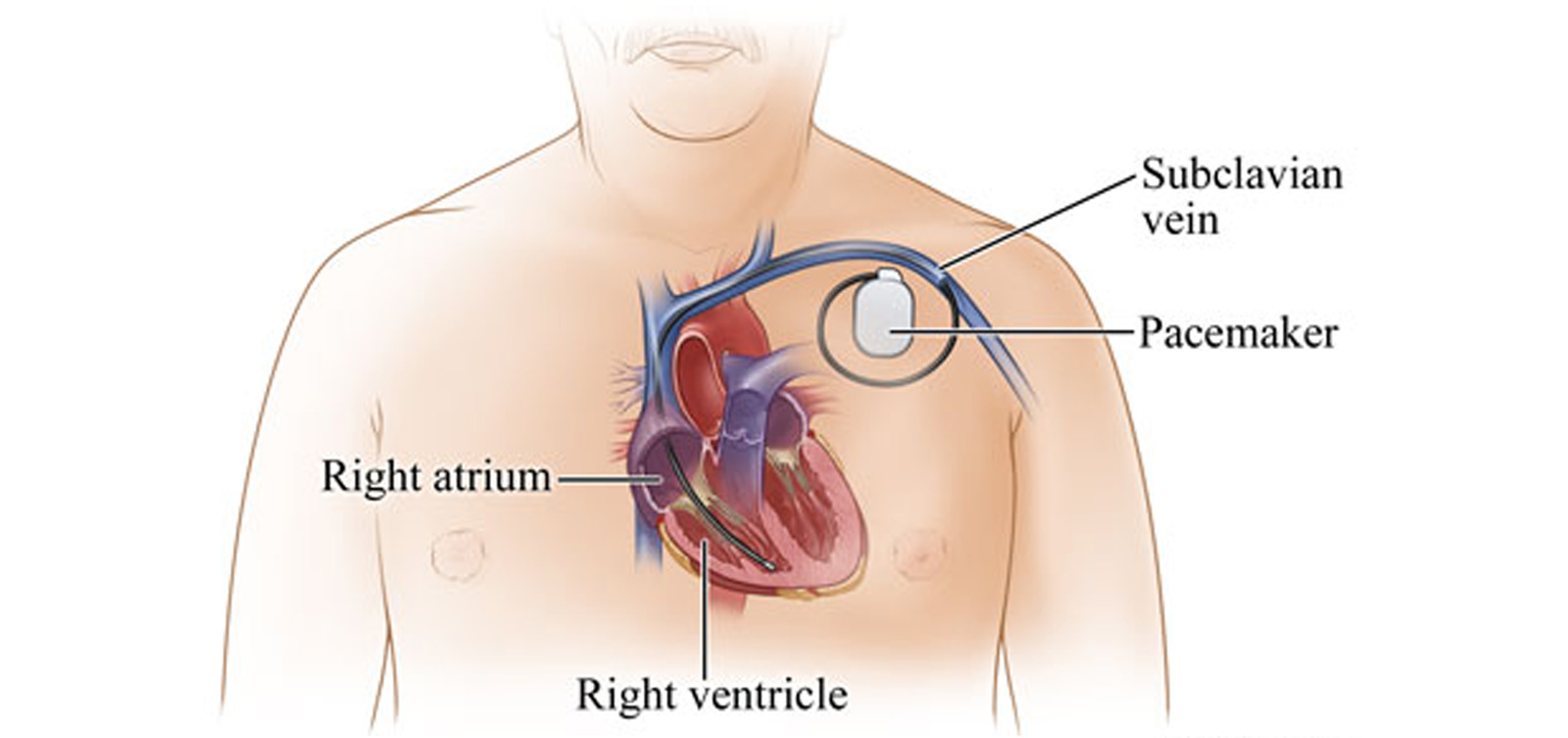
Temporary Pacemaker Implantation (TPI) is a critical procedure used in hospitals to stabilize patients experiencing severe heartbeat irregularities. This blog will provide an overview of TPI, including its purpose, indications, procedure, and potential side effects.
What is Temporary Pacemaker Implantation (TPI)?
TPI is a temporary medical intervention that helps regulate the heart’s electrical activity. It is primarily used in emergencies or as a temporary solution before the placement of a permanent pacemaker.
During the procedure, an electrode wire is inserted into the heart and connected to an external generator. This device delivers electrical impulses to the myocardium (heart muscle), ensuring a stable heart rate, proper circulation, and preventing complications caused by arrhythmias.
When is a Temporary Pacemaker Needed?
Temporary Pacemaker Implantation (TPI) is performed in several critical situations where immediate intervention is required to manage life-threatening arrhythmias or prevent complications. Some common reasons for using a temporary pacemaker include:
1. Severe Bradycardia
Conditions like sick sinus syndrome, heart block, or drug-induced bradycardia can cause the heart rate to drop below 60 beats per minute, posing serious health risks. TPI helps restore a normal heart rhythm in such cases.
2. Post-Myocardial Infarction Complications
After a heart attack, especially if the right coronary artery is affected, damage to the heart’s electrical system can cause conduction blockages. A temporary pacemaker may be required until the condition stabilizes.
3. Post-Surgical Support
During or after major surgeries, especially cardiac procedures, TPI can help regulate heart rhythm and maintain adequate blood circulation, reducing complications.
4. Electrolyte Imbalances and Medication Effects
Severe imbalances such as hyperkalemia, hypokalemia, or drug-induced bradycardia (from medications like beta-blockers or digoxin) may require temporary pacing to prevent dangerous slow heart rhythms.
5. Tachycardia Management
In certain cases of rapid heartbeats (tachycardia), a temporary pacemaker can help control and stabilize the heart rate when other treatments are ineffective.
Temporary Pacemaker Procedure: Step-by-Step Guide
Temporary pacemaker implantation is typically performed in a hospital under strict sterile conditions. Below is an overview of the procedure:
1. Pre-Procedure Preparation
• A thorough patient evaluation is conducted, including an electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood tests to determine the need for pacing.
• The patient is monitored continuously, and sedation is administered to ensure comfort while keeping vital signs and heart rate under observation.
2. Selecting an Access Site
• A catheter is inserted into a vein, usually the jugular, subclavian, or femoral vein, to guide the pacing lead.
• Using fluoroscopy (X-ray guidance) or ECG tracking, the lead is carefully positioned in the right ventricle to ensure proper placement.
• The lead is then connected to an external pacing device, which is calibrated to deliver the appropriate electrical impulses.
3. Post-Procedure Monitoring
• Patients are closely monitored for potential complications, including infection, bleeding, or lead displacement.
• Pacemaker settings are periodically adjusted based on the patient’s condition to ensure optimal heart rhythm regulation.
Temporary Pacemakers for Heart Conditions
Temporary pacemakers play a crucial role in stabilizing heart rhythm during medical emergencies, ensuring the heart continues to pump oxygen-rich blood to vital organs. Although not a permanent solution, Temporary Pacemaker Implantation (TPI) serves as a bridge therapy, allowing doctors to diagnose the underlying cause of arrhythmias and prepare for long-term treatment options, such as permanent pacemaker implantation or other necessary interventions.
Potential Complications of Temporary Pacemaker Implantation
Like any medical procedure, Temporary Pacemaker Implantation (TPI) carries certain risks. While complications are rare when performed by experienced professionals, they can still occur. Here are some possible issues:
• Infection – There is a risk of infection at the insertion site, and in severe cases, it could lead to systemic infections like sepsis.
• Lead Displacement– If the pacing lead shifts from its intended position, it may result in ineffective pacing or loss of function.
• Cardiac Perforation – Incorrect lead placement can puncture the heart wall, leading to serious complications such as cardiac tamponade.
• Vascular Complications – Accessing veins can sometimes cause bleeding, hematomas, or venous thrombosis.
• Electrical Malfunctions – Device-related issues, such as battery failure or incorrect settings, may interfere with proper pacemaker function.
• Arrhythmias – In some cases, the pacemaker itself may trigger irregular heart rhythms, either during lead placement or due to improper settings.
Though these risks exist, careful monitoring and expert handling significantly reduce the chances of complications, ensuring patient safety and effective treatment.
Advancements in Temporary Pacemaker Technology in Cardiology
Cardiology has seen significant progress in the field of temporary pacing, with innovations improving both the tools and techniques used. Modern external pacemakers now offer multiple pacing modes, tailored to meet the specific needs of each patient. Fluoroscopic guidance, along with real-time ECG tracking, has greatly enhanced the precision of lead placement, leading to a reduction in complications associated with temporary pacemakers.
Additionally, the emergence of wireless temporary pacing systems promises even greater benefits, including a lower risk of infection and more straightforward management, offering a promising future for patients requiring temporary pacing solutions.
Conclusion
Temporary pacemaker implantation (TPI) plays a vital role in managing severe arrhythmias and heart rhythm disorders, offering a life-saving solution in critical situations. While TPI is a temporary measure, it stabilizes the patient’s heart rhythm, providing the necessary time for doctors to address the underlying cause or pursue more permanent treatments.
Understanding the timing, procedure, and potential complications of TPI is essential for both patients and healthcare providers in recognizing its significance in cardiac care. Oxford Hospital stands out as one of the leading heart hospitals in Jalandhar, making it an excellent choice for those in need of temporary cardiac pacing. With advanced facilities, expert cardiologists, and a compassionate team, Oxford Hospital ensures optimal outcomes for all cardiac treatments, including temporary pacemaker implantation.





